What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a simple tool that helps businesses transfer important documents across different computer systems or networks. The heart of EDI is its ability to improve communication between businesses, making things easier and quicker. This function, handled by Electronic Data Interchange providers, uses a shared format that helps different systems understand the same data. Think of it as everyone speaking one language, even though they’re using various systems.
Picture a usual business situation where lots of documents like invoices, orders, or shipping details have to move between several entities. The old-fashioned way of doing this would involve a mountain of paperwork, repeated manual entries, and countless hours, leading to possible mistakes and delays. This tool helps companies avoid these obstacles, turning these documents into a shared format that can be sent electronically and understood by various systems. This allows for effective and quick document exchange between business partners, with little to no human involvement.
With the rise of the internet and network tech improvements, EDI has come a long way. Today, Electronic Data Interchange Companies offer advanced, cloud-based EDI solutions. These provide live data exchange and better connectivity.
What are EDI Solutions?
Picture a conference where everyone speaks a different language. Now, imagine a tech tool that translates everyone’s words into a universal format instantly. This is exactly what EDI Solution Providers do for companies. They transform business documents into a uniform format, making sure that communication between different systems is smooth and quick.
Basically, an EDI solution is a service or tool offered by EDI Software Providers. This tool enables the digital transfer of business documents in a uniform format. It automates the conversion of various data formats into one that’s universally understood. This allows businesses to share data effortlessly, no matter the systems they use.
The phrase “EDI solutions” is wide-ranging and includes a variety of services and software. Examples are cloud-based EDI, direct EDI, web EDI, mobile EDI, and others. These solutions serve a range of business needs, from small firms wanting to simplify their supply chain to large corporations looking to automate their whole business process.
What are EDI Services?
EDI Services mean a broad range of things offered by EDI service providers. It’s more than just giving software solutions. It’s about supplying a full method that looks after all EDI-related needs, making a united and smooth business talk space.
In simple words, these services are various kinds that assist businesses in setting up and managing their EDI systems well. These services are given by skilled EDI Service Providers in the USA and around the world. Their aim is to aid businesses in making the most out of their EDI money put in.
EDI’s role in the current business world is like an orchestra’s conductor. They make sure all parts of a company’s EDI system work well together, boosting efficiency and effectiveness.
Adopting EDI lets businesses pay attention to their main competencies. It leaves the details of EDI management to the pros. This leads to better work efficiency, cost savings, and smoother business talk. Plus, these services can often be changed and made to order. This lets businesses pick a solution that best suits their unique needs and goals.
1. EDI Outsourcing
Outsourced EDI Services are services that let businesses give their EDI tasks to expert third-party providers. These specific EDI Outsourcing Companies deal with various EDI aspects. This ranges from data translation and talks to compliance and system maintenance. They supply the technology, skills, and resources needed to manage EDI well. This frees up the business to focus on its main work.
For example, a retail business may want to unite its inventory system with EDI. This automates inventory updates from its suppliers. Instead of putting money into its own EDI structure and staff, the business can outsource these tasks to an EDI service provider. This provider ensures the smooth exchange of inventory data between the business and its suppliers. This leads to real-time inventory updates and better supply chain efficiency.
2. EDI Consulting
EDI Consulting is advice given by experienced Electronic Data Interchange Consultants. These consultants give expert advice on setting up and improving EDI systems. This advice is based on a business’s unique needs and goals. They look at a business’s current work, spot areas where EDI can add value, suggest suitable EDI solutions and assist in their setup and management.
For example, a manufacturing business may have inefficiencies in its order processing due to manual data entry and mistakes. An EDI consultant can study the business’s order processing workflow. They can suggest how EDI can automate and streamline this process. They guide the business in setting up the recommended EDI solution.
3. EDI Managed Services
EDI Managed Services involve a service provider taking full control of a company’s EDI system. This includes everything from setting up the EDI structure, making sure data complies and monitoring EDI transactions, to giving user support and system updates.
For example, consider a healthcare provider that wants to implement EDI for safe and compliant exchange of patient information. An EDI-managed service provider can set up the needed EDI structure, ensure the data exchanged complies with healthcare data standards and rules, monitor EDI transactions for issues, and provide ongoing user support and system updates.
4. EDI Staffing
EDI Staffing services involve finding skilled EDI pros for businesses. These services help businesses build competent in-house EDI teams by finding and recruiting people with the needed EDI knowledge and experience.
For instance, a big corporation that wants to manage its EDI work in-house might need to recruit EDI analysts, developers, and project managers. An EDI staffing service provider can help the corporation spot these staffing needs, find suitable candidates, and assist in the recruitment process.
5. EDI Support Services
EDI Support Services provide ongoing help for EDI systems. These services address any issues or challenges that come up with an EDI system. This ensures it stays working and effective. Support services may include troubleshooting, system updates, user training, and more.
For example, a logistics company that uses EDI for shipment tracking might face issues with data transmission or system updates. An EDI support service provider can help the company fix these issues, provide necessary system updates, and train users on new features or procedures. This ensures the EDI system continues to support the company’s shipment tracking effectively.
Types of EDI
Direct EDI
Direct EDI is like a digital handshake between two firms. It allows quick, safe, and exact sharing of data.
This type of EDI is fast and offers a lot of control. Companies can send data to partners right away, which is handy when time is crucial.
There are many perks of using Direct EDI. The top one is skipping the need for a middleman, saving money, and keeping data private. However, it requires a lot of tech knowledge, and setting up unique links with each partner can be tough.
EDI VAN
EDI VAN services are like online post offices. They collect, store, and send digital papers. Top EDI VAN providers like IBM, OpenText, and TrueCommerce are some examples.
EDI VANs enhance business talks by offering security, storage abilities, and a common communication rule. These services help different firms work together smoothly, despite using various internal data structures.
The main benefit of EDI VAN is its simplicity. It makes EDI chats easy and reduces the need for tech know-how. The downside is its price. Most providers charge based on the data size, which can get high for big firms.
Web EDI
Web EDI means doing EDI via an internet browser. Firms offering Web EDI solutions give a platform where firms can log in and share papers.
Web EDI changes EDI papers into a format that humans can read and shows it on a webpage. It works like an online mail system: log in, write a message and send it to the receiver you want.
Web EDI is user-friendly and easy to reach. EDI web services can be used from any gadget with an internet link. However, it is usually less automated than other EDI forms, which could raise labor costs.
Cloud EDI
Cloud EDI mixes the ease of Web EDI with the strength of cloud computing. EDI cloud solutions can deal with lots of papers without needing big physical structures.
Cloud-based EDI services offer strong solutions for data sharing. They provide EDI abilities without needing in-house servers or software, which is great for firms of all sizes.
Cloud EDI offers scalability, easy access, and low hardware costs. However, firms must make sure their EDI cloud services provider makes security a top priority to safeguard sensitive data.
AS2 EDI
AS2 EDI is a rule designed to send data safely and reliably over the internet. An AS2 EDI connection makes sure the data sent is both encrypted and signed, proving its safety and realness.
AS2 EDI provides a safe and efficient way to transfer data, using digital certificates and encryption to protect sensitive info.
EDI AS2 is well-known for its ability to safely send data over the internet. However, it needs a lot of technical expertise for setup and maintenance.
How does EDI work?
Step One: Assembling the Documents
Electronic Data Interchange Providers’ goal is to gather and organize all essential information, shifting it from paper to electronic files. Think of it this way: instead of physically printing a purchase order, your computer system creates an electronic file, crafting the blueprint for an EDI document.
There are many sources and ways to create these documents, providing several possibilities. Data can be entered by hand, or it can be pulled from spreadsheets and databases. Electronic reports can be reshaped into data files, or existing programs can be improved to automatically create files ready to be converted into an EDI standard. Plus, you can purchase software with built-in EDI file interfaces, making your shift to the EDI world smoother.
Step Two: Converting to EDI Format
Once the data is neatly arranged, the next step kicks in. This step changes your internal data format into the EDI standard format. Consider this as a language converter, helping your business to connect smoothly with others worldwide. EDI translation software, much like an expert language interpreter, reshapes your internal data into the universally recognized EDI language.
This software can be handled in-house and kept on your premises, although it requires mapping know-how to decide how your internal data matches with the EDI data. The bright side is that EDI Service Providers in the USA offer a broad array of translation software suitable for various settings and budgets.
On the other hand, you might think about using an EDI service provider’s translation services. It’s like outsourcing your laundry—you send your data to the provider who manages the conversion into EDI format, making the process simpler and saving you time.
Step Three: Connecting and Transmitting the EDI Documents
The last step in the EDI process of Affordable EDI Solutions is much like a postal service – linking and sending your EDI documents to your business partner. At this point, your business documents have been converted to the correct EDI format and are ready to be sent.
There are many ways to handle this process. One option is to directly connect using a secure internet protocol such as AS2, or you could connect to an EDI Network provider and count on them to connect to business partners using their preferred communications protocol. Some businesses pick a mix of both based on the specific partner and the number of transactions to be swapped.
What are the Benefits of EDI?
Embracing Efficiency with EDI Solutions
In our modern, tech-centered era, businesses flourish when they make use of cutting-edge tools that simplify operations and raise efficiency. One such potent instrument that’s revolutionizing business tasks around the world is Electronic Data Interchange or EDI. Taking on complete EDI solutions can significantly upgrade your business output, enhancing pace, accuracy, and overall productivity.
At its heart, EDI is a digital communication method that offers a uniform format for swapping business documents. By taking advantage of EDI, firms can save both time and resources. It achieves this by automating activities traditionally done by hand. In turn, businesses experience a notable decrease in operational costs and an uptick in transaction speed. Thus, EDI emerges as a key resource in strategic business growth.
Cost Savings with EDI Software Solution
Switching from traditional document processing to an EDI software solution unlocks considerable financial gains. Electronic document exchange does away with the need for manual work, drastically cutting costs. Plus, EDI software gets rid of expenses linked with paper, printing, copies, storage, filing, postage, and document search. The outcome? A 35% reduction in transaction costs, at least.
One striking case of this cost-effectiveness comes from a leading electronics producer. They found that processing an order manually amounted to $38. In contrast, the same order processed using EDI was a mere $1.35. Such vast savings underscore the huge financial edge of integrating EDI solutions.
Boosting Accuracy and Speed with EDI Integrated Business Solutions
Along with saving money, EDI integrated business solutions notably lift the speed and precision of business tasks. These solutions can speed up business cycles by 61%, allowing transactions to happen in minutes rather than the days or weeks it takes through postal services. Additionally, EDI-integrated businesses have demonstrated an improvement in data quality, yielding a 30-40% decrease in transactions with errors.
A key advantage of EDI is that it cuts the order-to-cash cycle time by over 20%. This increase in efficiency improves business transactions and also builds stronger relationships with business partners.
Improving Business Efficiency through EDI Service
EDI service sets the stage for substantial enhancements in business efficiency. Automating paper-dependent tasks allows staff to concentrate on more value-added activities, thereby raising productivity. Quick and accurate document processing results in fewer order cancellations and stock-outs, thus improving operational efficiency.
Moreover, EDI services can automate data swaps between apps across a supply chain. This assures the timely transfer of essential business data, thereby improving cash flow, reducing order-to-cash cycles, and enabling real-time data tracking.
Transforming Business Strategy with EDI Service Providers
EDI service providers can trigger transformative changes in business strategy. With real-time visibility into transaction status, businesses can make faster decisions and respond better to changing customer and market demands. This agility lets companies take up a demand-driven business model as opposed to a supply-driven one.
In addition, EDI lets businesses streamline their entry into new markets by offering a shared business language that facilitates easy onboarding of business partners worldwide. Plus, it promotes corporate social responsibility and sustainability by swapping paper-based processes with electronic alternatives, thus lowering a company’s carbon footprint.
Industry Use Cases of EDI
EDI in Healthcare
Healthcare is a fast-moving world. It needs quick, correct, and private data. EDI helps with this. It makes the sharing of medical data easier.
A good example of EDI in healthcare is sending patient records. In the past, this required paperwork. It was slow and could be wrong. Now, with EDI, doctors can quickly and correctly send health data. This can be lab results or prescriptions. It is sent between health centers. It makes patient care better by avoiding mistakes.
EDI also helps with medical billing and claims. It lets claims be sent to insurance companies electronically. This means payments are made quicker. It cuts down on costs and makes work easier. It lets healthcare workers focus on patient care.
EDI in Insurance
Insurance is another area where EDI is very useful. Insurance deals are complex. They involve a lot of paperwork. So, automatic data sharing is needed. EDI helps insurance companies process claims more quickly and efficiently.
EDI is also important in managing policies. It makes sharing policy data between agents, brokers, and insurers easier. This makes issuing and renewing policies faster. It improves customer happiness.
Finally, EDI improves data accuracy in insurance. It gets rid of manual data entry. This reduces the chance of mistakes. It helps build trust and transparency between insurance companies and clients.
EDI in Finance
The finance sector needs quick and correct data sharing. EDI helps with this. It makes the financial supply chain more efficient. It includes tasks like receiving invoices, starting payments, and sharing settlement details. This cuts costs and mistakes tied to traditional paper methods.
EDI also helps in handling international financial deals. The global finance world deals with different currencies, rules, and accounting methods. EDI acts as a bridge to reconcile these differences. It makes cross-border transactions easier.
Lastly, EDI supports different file formats and communication protocols. This ensures smooth financial data transfer worldwide. It sticks to standards set by groups like SWIFT, ISO, and NACHA.
EDI in Retail
In retail, EDI is revolutionary. It helps manage huge volumes of transactions. EDI is very useful in inventory management. It gives real-time data on stock levels. This helps retailers avoid having too much or too little stock. As a result, they can maintain ideal inventory levels.
EDI also makes order processing faster in retail. Automated data exchange allows faster customer order processing. This leads to quicker deliveries. This speed is crucial in today’s world of same-day deliveries and instant gratification.
EDI in Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector depends on timely raw material delivery and quick dispatch of goods. Here, EDI acts as an enabler. It ensures efficient communication between manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors.
One main use of EDI in manufacturing is in supply chain management. Automated order placements and shipping notices help better manage the supply chain. This leads to improved efficiency and cost reduction.
Lastly, EDI helps in production planning. Manufacturers can get real-time data from suppliers on raw material availability. This helps them plan production schedules more accurately.
EDI Documents
EDI documents adhere to specific rules and structures. They’re made up of various parts like data elements, segments, and envelopes. Let’s understand these elements.
The Fundamental Building Blocks: Data Elements
Picture a data element as the tiniest unit of information in an EDI document. These units hold details like city, state, country, item number, quantity, and price. You can liken it to cells in a spreadsheet, each carrying some information.
The EDI Standard decides what type of data a data element represents. It could be numeric, alphanumeric, date, or time. Also, it sets the shortest and longest length for each data type. Sometimes, certain codes must be followed. Like, for stating a unit cost, a currency code to show the type of currency is needed.
Grouping Data Elements: Segments
In an EDI document, similar data elements are bunched into segments. Think of a purchase order form split into sections like ‘Buyer Details,’ ‘Order Summary,’ ‘Item Details,’ and so on. In EDI, each of these sections would be a segment.
For instance, an EDI document might have segments labeled by ID codes like ST (transaction set header), BEG (beginning segment), and N1 (name). Every segment starts with an ID code, then comes related data elements. The standard for each business document says which segments are needed, optional, or dependent. It also sets the sequence of segments and how often a segment can be repeated.
Assembling Segments: Transaction Sets
A Transaction set, or a “message,” is the full EDI document. It has all the necessary segments in the right order. Think of it as a full business document like a purchase order or an invoice. The gathering of all segments in a specific order makes a transaction set ready for sending.
Packaging for Delivery: EDI Envelopes
Just as paper documents go into an envelope before mailing, EDI documents also need enveloping before sending. The enveloping system for EDI has three stages – the Message envelope, the Group envelope, and the Interchange envelope.
Each transaction set gets its envelope. Then, a bunch of related transaction sets go into a group envelope. This is a must in ANSI (American National Standards Institute) and optional in EDIFACT (Electronic Data Interchange For Administration, Commerce, and Transport). Lastly, all group envelopes for one recipient go into an Interchange envelope.
The start and end of an envelope are marked by a pair of segments. For instance, in the EDIFACT standard, the segments UNH and UNT make the Transaction Set Envelope, UNG, and UNE shape the Group Envelope, and UNA/UNB and UNZ form the Interchange Envelope.
EDI Implementation
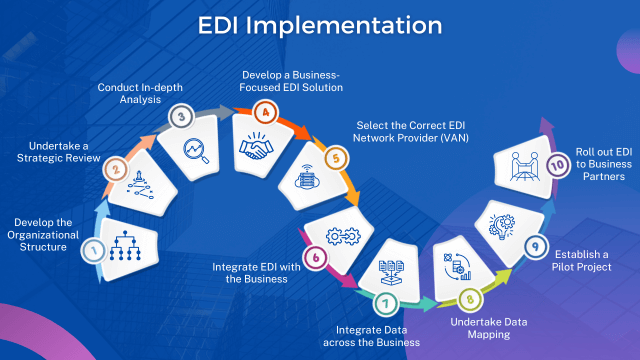
Implementing EDI requires careful planning and execution. The following is a clear and concise explanation of a structured 10-step process for a successful EDI implementation.
Step 1: Develop the Organizational Structure
The backbone of any EDI implementation lies in its organizational structure. Three key elements of this structure are:
The EDI Coordinator: This individual is in charge of steering the EDI initiative within the organization, maintaining open communication with all sectors affected by the EDI program. This liaison role ensures support and buy-in from all departments, highlighting the benefits and implications of the EDI program.
The Steering Committee: This team guides the overall direction of the EDI implementation, setting objectives and overseeing progress.
Dedicated EDI Team: This team is responsible for executing the EDI strategy, monitoring its ongoing function, and troubleshooting any issues that arise.
Step 2: Undertake a Strategic Review
Next, organizations must conduct a strategic review to identify applications for EDI deployment and prioritize their conversion. This step entails considering factors such as the number of business partners and the volume and type of transactions. By assessing current systems and envisioning how EDI could enhance them, the strategic review ensures an effective implementation process.
Step 3: Conduct In-depth Analysis
An in-depth analysis aims to answer critical questions about the organization’s readiness for EDI, the cost of implementation, and the potential savings. Tools like Cost Benefits Analysis (CBA) and EDI Surveys can provide invaluable insights during this stage, aiding in cost justification and decision-making.
Step 4: Develop a Business-Focused EDI Solution
This step leverages the knowledge gained from the analysis stage to design a comprehensive EDI system. Elements such as expected EDI traffic, network infrastructure capacity, required programming, and necessary customizations come into play here.
Two core elements of any EDI system are:
The EDI Translator: This tool converts data into a format compatible with the EDI standards.
The Communications Model: This outlines how data will be transmitted and received between the organization and its business partners.
Step 5: Select the Correct EDI Network Provider (VAN)
Selecting a suitable EDI Network Provider is crucial. Companies should consider factors such as the provider’s industry influence, reach, pricing structure, and sustainability before making a decision.
Step 6: Integrate EDI with the Business
Once the system is set up, it’s time to integrate EDI with the business. This means making sure EDI becomes a seamless part of existing workflows and processes.
Step 7: Integrate Data across the Business
Data integration is the process of merging data from disparate sources to provide a unified view. In this step, the data flowing through the EDI system should be effectively integrated with the company’s existing databases and applications.
Step 8: Undertake Data Mapping
Data mapping is the process of linking fields from one database to fields in another. It is a crucial part of ensuring that data transferred through EDI is correctly understood and used on both ends of a transaction.
Step 9: Establish a Pilot Project
A pilot project is a small-scale, preliminary study conducted to evaluate the feasibility, duration, cost, and adverse events associated with EDI implementation. Through this pilot project, you can ensure the EDI system maintains adequate control, provides projected benefits, handles anticipated EDI traffic, and satisfies internal users.
Step 10: Roll out EDI to Business Partners
Once the pilot project has been proven successful and any necessary adjustments have been made, it’s time to roll out EDI to your business partners. This step marks the beginning of your new, more efficient digital business interactions.
Cost of EDI
It’s crucial to evaluate the costs involved in an EDI implementation. Essentially, you have two pathways: either creating your EDI infrastructure in-house or partnering with a third-party EDI provider. Each approach brings distinct financial implications. Therefore, it’s imperative to be well-versed with them to drive the maximum value for your business.
The EDI Provider or Value-Added Network (VAN) Route
Third-party EDI providers or VANs present a cost-effective avenue to adopt EDI, especially for businesses lacking the requisite resources to develop an in-house infrastructure. However, it’s not as simple as picking the cheapest provider. There are myriad business factors to deliberate on before making a decision.
A fundamental consideration is the number of your business partners already present on the provider’s network. This factor could significantly impact the cost and ease of integrating your supply chain into the EDI environment. Additionally, the provider’s geographic coverage plays a significant role in your operations span across multiple countries.
Next, it’s necessary to scrutinize the level of support and training the provider offers. This aids in a smoother transition to EDI for you and your trading partners. Another key criterion is the array of options the provider offers to enable all stakeholders to use EDI effectively.
The cost typically hinges on the volume of data you transmit over the network, commonly measured in kilo-characters (KCs) contained within your EDI document. Providers often propose various pricing models, such as pay-as-you-go, monthly, or annual subscriptions. Be cautious about hidden charges tied to minimum record lengths, and ensure to evaluate your transaction volume and nature before opting for a provider.
Lastly, be discerning while evaluating providers offering “free” EDI VAN services. It’s crucial to read the fine print as such services are often not free in reality.
Navigating the In-House EDI Path
For large organizations with significant resources, creating an in-house EDI network might seem an attractive option. It offers control, security, and the luxury of internal management. However, this route is not without challenges and requires a substantial investment.
You’ll need to set aside funds for EDI software, communication tools, mapping and translation software, and specialist personnel. Moreover, continuous upgrades, support, and maintenance are integral to keeping your EDI system up-to-date and functional.
Establishing an in-house EDI system is merely the starting point. You’ll need to support each of your business partners to implement the system at their end. This becomes an ongoing requirement as your trading community evolves, grows, and changes.
Owing to these substantial investments and complexities, many businesses opt to collaborate with a third-party provider who can offer the EDI infrastructure without the significant upfront investment. This is especially beneficial for small and medium-sized enterprises that might not have the necessary resources.
EDI Transactions
EDI, short for Electronic Data Interchange, is about swapping business documents in a standard digital layout. It’s like a computer chatting with another computer. This chat or exchange is what we call EDI transactions. These transactions have transformed the way businesses talk to each other. They could be the secret sauce to boost efficiency and save costs.
Let’s step into the world of EDI transaction codes. These codes act like name tags for certain documents within the EDI system. Each business document, like invoices, purchase orders, or shipping updates, has its own unique EDI transaction code. These codes bring harmony and lower the chances of mistakes. They avoid the mix-up that could happen if different businesses used different names for the same document.
Now, what are EDI transaction sets? They’re like packages of linked documents sent together. Imagine a package with a purchase order, an order approval, and an invoice. These packages have their own unique codes and are designed for easy handling. The structure of these sets is generally standard and approved by the trading partners involved.
One standout benefit of these sets is their impressive efficiency in dealing with many linked documents at once. This method is a real time-saver. Plus, it cuts down the chances of data entry errors. So, it guarantees a smoother and more trustworthy swap of business documents.
EDI transaction types. Some common ones are invoices (EDI 810), purchase orders (EDI 850), and advanced shipping updates (EDI 856). Each type represents a different stage in the supply chain process. They help businesses to talk clearly and effectively. Knowing the different EDI transaction types can help organizations smooth out their operations and avoid miscommunication.
EDI Transactions in Healthcare
Let’s now discuss EDI in Healthcare. Healthcare EDI transactions streamline and simplify the handling of health records. This boosts the overall efficiency of the healthcare system. They lower the chances of human error tied to manual data entry. They also cut down administrative overheads, saving healthcare providers a lot of time and money. Plus, they speed up the handling of insurance claims and repayment. This leads to better service for patients.
To get a better idea of EDI transactions healthcare, we need to know some standard components. Some of the most common ones are healthcare claims or matching encounter info (EDI 837), healthcare eligibility benefit inquiry and reply (EDI 270/271), and healthcare claim status request and reply (EDI 276/277).
Each of these transaction types has a specific role in healthcare. For example, the EDI 837 document lets healthcare providers submit medical claims to insurance companies electronically. This cuts down the time needed for claim handling and repayment.
So, what’s the big deal about these EDI healthcare transactions? The magic is in its power to ease the flow of correct, real-time data across the healthcare system. This quick info swap boosts decision-making, allows instant feedback on insurance claims, and guarantees fast patient care. So, healthcare providers can focus more on their main job – providing top-quality healthcare services.
EDI 834
EDI 834, or the Benefits Enrollment and Maintenance document, plays a critical role in the healthcare industry. Think of it as a vital bridge between employers, insurance companies, and benefit enrollees. This document enables employers and insurers to exchange details about benefit plan enrolment. It provides information such as the enrollee’s identification, plan details, and effective dates. Thus, EDI 834 ensures that benefit plans are executed correctly, and participants receive the coverage they’re entitled to.
EDI 837
When a patient receives healthcare services, providers need a way to communicate with insurance companies about the care given and the payment due. This is where the EDI 837 document steps in. It’s akin to an electronic invoice that healthcare providers send to insurers. It contains details about the patient, the provider, the services rendered, and the charges for these services. Utilizing EDI 837 not only speeds up the billing process but also reduces the chances of errors that may occur with manual data entry.
EDI 835
Imagine you’re an insurer who has just received an EDI 837 document. Now you need to respond – either to make a payment or to explain why a claim is denied. This response is the EDI 835, also known as the Healthcare Claim Payment/Advice document. It provides detailed remittance information about the claims payment and information to simplify the balance reconciliation process. Thus, EDI 835 plays a crucial role in facilitating smooth and efficient communication between healthcare providers and insurers.
EDI 270-271
Before healthcare services are rendered, there’s often a need to verify a patient’s eligibility for specific treatments or benefits. The EDI 270 document serves this purpose. A healthcare provider sends this inquiry to an insurer to check a patient’s coverage. The insurer then replies with the EDI 271 document, giving the details of the patient’s eligibility and benefits. Together, the EDI 270-271 transaction pair ensures that providers have the information they need before rendering services, thus preventing potential disputes or complications down the line.
EDI Standards
HIPAA EDI
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a landmark law enacted in the United States. One of its significant components includes the establishment of standards for electronic healthcare transactions, commonly known as HIPAA EDI. These standards mandate how certain health-related information is electronically exchanged between entities such as hospitals, insurance companies, and health service providers.
HIPAA EDI simplifies and standardizes the complex process of handling healthcare data, ensuring seamless and secure data transmission. It specifies how each document type should be formatted and what information it should contain. For instance, a HIPAA EDI-compliant health insurance claim document must include details like the patient’s identification, the services provided, and the claim amount. This standardization helps streamline administrative tasks, leading to improved efficiency and reduced costs.
UN/EDIFACT
Next, let’s delve into UN/EDIFACT, an acronym for United Nations Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport. This is the international EDI standard developed under the United Nations. UN/EDIFACT is widely used in global trade, facilitating easy and standardized data exchange across countries.
The UN/EDIFACT standard encompasses a wide range of business documents, such as invoices, shipping notices, and purchase orders. It plays a vital role in global trade, ensuring consistent, reliable, and efficient communication between international trading partners. It aids in reducing errors and misunderstandings that can occur due to language barriers or different data formats.
ANSI X12 EDI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) X12 EDI, often shortened to ANSI X12, is a prominent standard used primarily in the United States. This EDI standard was developed to facilitate electronic data interchange between businesses. From healthcare to finance, retail to transportation, ANSI X12 covers a wide array of industries.
Like other EDI standards, ANSI X12 provides a common language for businesses to exchange crucial data. It offers a uniform structure for electronic documents, ensuring that all parties involved can accurately interpret the information being exchanged. This consistency helps improve overall business communication, promoting accuracy and efficiency.
EDI AS2
Applicability Statement 2, better known as EDI AS2, is a standard that provides a secure framework for transmitting data over the Internet. AS2 creates an “envelope” for EDI data, allowing it to be sent securely using digital certificates and encryption.
EDI AS2 is widely recognized for its robust security measures, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality. It ensures that the data exchanged is untouched and unreadable by unauthorized parties. Moreover, it includes a feature called “Message Disposition Notification” (MDN), which serves as a digital receipt, confirming successful data transmission.
EDI Integration
EDI, or Electronic Data Interchange, is like a magic key for businesses. It allows them to share important documents and data without any hitches. Imagine it as a common language that every company speaks. No matter what different systems they use, EDI makes sure they all understand each other. It’s like having a superhero translator working around the clock to keep communication clear and quick.
The term “EDI Integration” may sound complex, but its role is pretty simple. It helps move and translate data between separate software applications or systems. Picture a line of dominos: when one domino moves, it affects the next one, making a smooth chain reaction. That’s what EDI Integration Services do in the business world. They connect different operations, systems, and processes for a smooth, efficient workflow.
The Power of API and EDI Integration
The merging of API and EDI Integrations has become a powerful duo in the world of data transfer and system linkage. Imagine an API as a restaurant waiter. He takes your order (or your data request) and delivers it to the kitchen (the system storing your data). The EDI is the expert chef preparing the order, ensuring it’s ready for delivery. Together, they ensure your data request is taken, prepared, and served quickly and correctly.
EDI Integrated Business Solutions
The EDI Integrated Business Solutions are like a handy toolbox for corporations. They offer many functions that make things efficient and cut out mistakes from manual processes. EDI is like a superhero who can multitask, helping businesses handle various tasks – from supply chain operations to invoicing – all at once. It links systems, supports automation, and promotes real-time communication. Simply put, it’s the lubricant that keeps a business machine running smoothly.
Lastly, EDI Integration Solutions are like a magical answer to companies looking for better data management. It’s like finding the perfect suit: custom-made to suit your unique needs, versatile for different events, and always making sure you present your best. In the business world, “presenting your best” means efficient operations, flawless data exchange, and the capacity to grow and adapt to your business.
EDI is the invisible conductor leading a perfect orchestra of data exchange, allowing companies to focus on their main goal – innovating and growing their business.
The Future of EDI
Ever since the dawn of EDI, short for Electronic Data Interchange, this technological marvel has remained a cornerstone in several industries for more than half a century. The tale of EDI’s birth dates back to 1948, when an Army Master Sergeant, Ed Guilbert, conceived a paper-based system for EDI that allowed for the organized transportation of colossal quantities of goods. A full two decades later, this concept metamorphosed into electronic messages – the bedrock of modern EDI.
As we delve deeper into the past, it becomes apparent that EDI has always been a work in progress. The year 1968 marked a significant milestone in its evolution as the Transportation Data Coordination Committee (TDCC) developed electronic standards, paving the way for EDI norms that are prevalent across myriad industries, including automotive, manufacturing, healthcare, and retail.
Turning Points and Constant Evolution
A noteworthy turning point for EDI came in 2002 when XML and AS2 standards were introduced. Initially, these were believed to be the harbingers of the demise of EDI. They promised an ostensibly superior alternative to EDI, with XML being human-readable and AS2 quickly adopted by retail Titan and Walmart. However, rather than upending EDI, these protocols added more diversity and intricacy to digital trade, further solidifying EDI’s position.
Fast forward to 2019, EDI was still at the helm of B2B electronic sales, accounting for a staggering 78.4%, which translates to a monumental $7 trillion. EDI, with its robust optimization for vital business processes, fortified its role in not only purchasing and invoicing but also production and supply chain operations.
The Emergence of Automation in EDI
In the wake of the global pandemic in 2021, the emphasis on automation has been put under the spotlight. Many organizations leveraged the power of cloud-based EDI VANs to automate their B2B processes, thereby smoothening digital business transactions throughout their trading partner community.
Given this trajectory, it’s projected that the healthcare industry alone will see the EDI market value skyrocket to $5.9 billion by 2025. This indicates an impressive annual growth rate of 9.4%. Undeniably, EDI continues to play an integral part in conducting business, and it’s expected to experience further growth as more businesses rely on it to streamline B2B connections.
Anticipating the Future of EDI
As we gaze into the crystal ball to anticipate the future of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), it’s clear that this transformative technology is well-positioned to continue its evolutionary journey. Despite being in existence for more than half a century, EDI’s relevance in today’s digital age is undisputed, and its potential for future adaptation and innovation remains promising.
Enduring Relevance and Adaptability
EDI, with its proven adaptability, is no stranger to changes in the business landscape. It has weathered technological disruptions, market fluctuations, and shifts in industry standards, emerging stronger and more resilient each time. Its longevity is a testament to its versatility and its ability to mold itself to the changing needs of businesses.
In the future, we can expect EDI to further cement its position as an essential tool for B2B transactions. As businesses continue to expand their digital footprint, the need for a reliable and efficient data interchange system will only grow. EDI, with its proven track record, is perfectly suited to meet this increasing demand.
Advancements in Integration and Automation
One area where EDI is poised to make significant strides is integration. The rise of complex technologies such as APIs and XML has broadened the scope of EDI, allowing for a higher level of connectivity and interoperability. For example, services like OpenText’s Trading Grid offer unified integration platforms that support intricate integration processes, not just for EDI but also for APIs and XML.
Automation is another realm where EDI is set to make a substantial impact. As we have seen, the recent trend towards automation, accelerated by the global pandemic, has propelled EDI to the forefront. In the future, we can anticipate more companies embracing EDI automation, thus increasing efficiency, minimizing errors, and promoting seamless B2B communications.
Growth and Expansion Across Industries
The market value of EDI is also projected to witness significant growth. According to estimates, the healthcare industry alone could see the EDI market worth ballooning to $5.9 billion by 2025, reflecting an annual growth rate of 9.4%. This growth trajectory is indicative of the rising reliance on EDI across various sectors. As industries continue to recognize the value of streamlined, efficient, and reliable data interchange, the adoption of EDI is likely to surge.
Conclusion
Grasping EDI is key for any business aiming to enhance its performance and get a leg up on rivals. EDI mechanizes data sharing, lessens human mistakes, quickens business activities, and nurtures healthier ties with associates. It’s like a top chef with the finest cookware, whipping up yummy meals with haste, precision, and effectiveness.
EDI tools and aids offer loads of perks, such as slashing costs, bettering efficiency, enhancing precision, and instant data sharing. With a wide array of aids at your disposal, businesses can adjust their EDI processes to match their unique objectives. It’s like carrying a Swiss Army knife – whatever the scenario, you have a handy aid.
In the end, adopting and wisely handling EDI tools paves a path for businesses to thrive in our speedy, data-centric business world. So, if you’re a small-scale business owner eyeing to streamline your supply chain processes or a global firm keen to better data accuracy and adherence, understanding and using EDI is the golden ticket to scaling new peaks of triumph.
Now that you hold a strong grip on EDI and its ability to transform, it’s time to take action. Welcome EDI today with the help of TopOrgs, and let it be your secret weapon in your journey towards business success. Connect with top EDI service providers and kick off your trip towards smooth, seamless, and efficient business communication. Because, at the end of the day, the path to business success is built on strong communication, and EDI is your chosen vehicle.